Authored by Aurinia Pharma U.S., Inc.
Lupus nephritis (LN), a common and serious complication of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), occurs when there has been damage to the kidney.1 Kidney damage may result in proteinuria, the leakage of proteins into the urine.2 The level of proteinuria often indicates the degree of kidney injury and is used as a reliable indicator of treatment effectiveness.3 Promptly treating your patients with LN to guideline-recommended proteinuria targets is recommended for improving their long-term health outcomes.
Importance of Rapid Reduction
The presence of protein in the urine has been shown to be independently associated with a greater risk of kidney failure and death.4
A long-term follow-up trial comparing mycophenolate mofetil and azathioprine as maintenance therapy showed that the reduction of proteinuria at 3, 6, and 12 months was highly predictive of a good long-term kidney prognosis.5 It was also shown that if 100 patients achieved a proteinuria level <0.5 mg/mg at 12 months, 92 of them would have preserved kidney function 10 years later.5
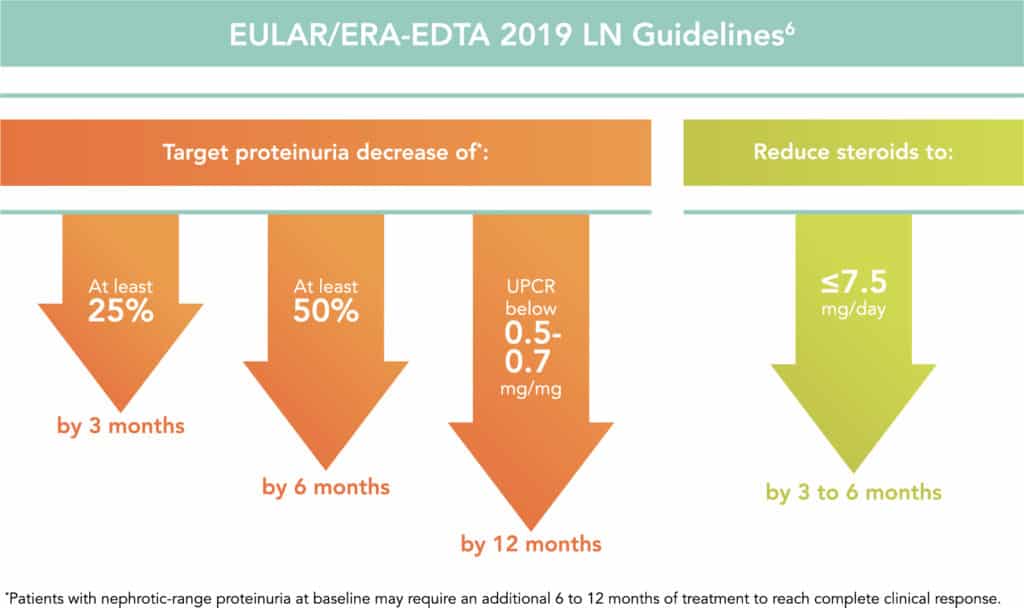
Treat to Target
Incorporating the current body of evidence, the most recent 2019 EULAR/ERA-EDTA guidelines for the management of LN recommend specific treatment targets to preserve kidney function.6 By 1 year after initiation of treatment for LN, physicians should target a urine protein-to-creatinine ratio (UPCR) below 0.5 mg/mg to 0.7 mg/mg.6
The guidelines also emphasize minimizing the cumulative steroid dose to reduce the risk of end-organ damage.6
Because time is of the essence with LN, guidelines recommend reducing proteinuria in your patients.
Visit TimeIsNephrons.com to learn more about the actions you can take to improve outcomes for your patients with LN.
At Aurinia Pharma U.S., Inc., our mission is to transform people’s lives by delivering therapeutics that change the course of autoimmune disease. Discover more about Aurinia at www.auriniapharma.com
ERA-EDTA=European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association; EULAR=European League Against Rheumatism; LN=lupus nephritis; SLE=systemic lupus erythematosus; UPCR=urine protein-to-creatinine ratio.
References: 1. Almaani S, et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;12(5):825-835. 2. KDIGO CKD Work Group. Kidney Int Suppl. 2013;3(1):1-150. 3. Palmer BF. Am J Nephrol. 2007;27(3):287-293. 4. Levey AS, et al. Kidney Int. 2011;80(1):17-28. 5. Tamirou F, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(3):526-531. 6. Fanouriakis A, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(6):713-723.
Copyright ©2021, Aurinia Pharma U.S., Inc.
All rights reserved. (10/21) US-NA-2100156












